In August this year, we released SELECTseries 4 of STAAD.Pro V8i. The
main enhancement included in this release was the introduction of the latest
AISC 360-10 steel design code. However, this did not include a few features
that were found to be required by many users that use the AISC code and has led
to production of a new patch release which is now available on the Bentley
SELECT servers. The key issues addressed include:-
- Deflection Checks,
Enhanced over other AISC deflection checks in that a design will only perform
deflection checks on those load cases classified as SERVICABILITY. - Automatic profile selection.
- Slenderness
Optional checks added with the MAIN and TMAIN parameters - Single angle section
Design about both principal and geometric axes.
The patch has additionally addressed issues in a number of other areas
and listed here and can be found in the ReadMe file installed with updates from
all other version:-
1. What's New in STAAD.Pro V8i SS4 patch, Build 20.07.09 ( 29 November
2012)
(A) Issues addressed in the Analysis/Design engine (36)
(B) Issues addressed in the Pre-Processing Mode (02)
(C) Issued Addressed in the Post-Processing Mode (02)
(D) Issues Addressed in the Steel Design Mode (00)
(E) Issues Addressed in the Concrete Design Mode (00)
(F) Issues Addressed in the RAM Connection Mode (00)
(G) Issues Addressed in the Advanced Slab Design Mode (00)
(H) Issues Addressed in the Piping Mode (00)
(I) Issues Addressed in the Editor, Viewer and other modules (00)
(J) Issues Addressed in OpenSTAAD (00)
(K) Issues Addressed with Printing and Documentation (06)
(L) Issues Addressed with licensing / security / installation (01)
(A) Issues addressed in the Analysis/Design engine (36)
A) 01 The deflection check has been introduced into the AISC 360-10 steel
design module using the parameters DFF, DJ1 and DJ2 as with previous codes, but
has been enhanced to allow deflection checks to be performed on different load
cases than the force checks, with the overall worst ratio being the governing criteria.
The load cases that are required for deflection checks should be included in a
load envelope that is defined as a ‘Serviceability’ case:-
. DEFINE ENVELOPE
. (load case and combination numbers) ENVELOPE (envelope number) TYPE
SERVICEABILITY
. END DEFINE ENVELOPE
If any of these load cases are then included in the AISC 360-10 design,
they will be used for deflection checks. All other load cases will be used for
force checks.
Note that if a deflection check is required, then the parameter DFF must
be set to the required value on the members that are to be checked for
deflection.
A) 02 The AISC 360-10 steel design code has been corrected to ensure
that if a SELECT command is included, then the design will run the select
process as outlined in the manual and implemented in all other design codes
including the previous versions of the AISC code.
A) 03 The ASIC 360-10 steel design module has been updated to address an
issue with sections that have been defined as welded using the parameter 'STP
2', these were not accounted for correctly and could cause the design to crash.
A) 04 The AISC 360-10 steel design module has been enhanced with the
reintroduction of the MAIN and TMAIN parameters. Setting either to 1.0 will
bypass any slenderness checks.
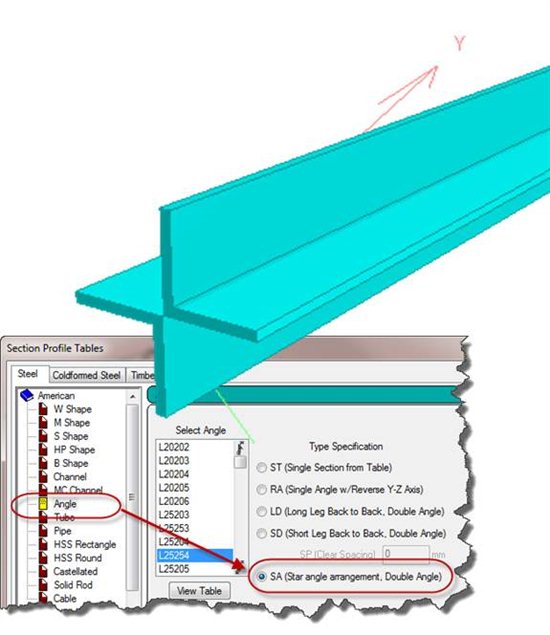
A) 05 The AISC 360-10 steel design module has been improved in the
design of single angle sections. The check of single angle profiles is now
reported in both geometric and principal axes and the most efficient design
used in the overall design.
A) 06 The AISC 360-10 steel design output has been corrected to reflect
the sign of axial force where a positive axial force is compression and
negative is tension. Note that this is only a report issue, tension and
compression forces were being used in their correct sense in the actual design.
A) 07 The AISC 360-10 steel design module has been improved to allow the
design of User Provided Table (UPT) tube profiles by calculating the design
torsion capacity which was previously returning zero and thus always failing
with utilization ratio of infinity.
A) 08 The AISC 360-05 design code has been updated to improve the web
shear coefficient Cv
A) 09 The AISC 360-05 steel design module has been improved for design
of pipes in User Provided Tables (UPT). These sections can include a definition
of shear area. However, previously the design would use a calculated shear area
rather than that specified in the user table. Now, if there is a value in the
user table, that value will be used.
A) 10 The AISC 360-05 steel design module has been improved with respect
to the section classification. Previously a worst classification would be
established and used throughout for each member design. Now, a classification
is established for each check as appropriate.
A) 11 The IS1893 seismic load generation has been updated to correct the
calculation of the static base shear used in VB/vb.
A) 12 The SOFT STOREY CHECK has been updated to ensure that the check is
performed correctly where the model is defined with exactly 4 storeys.
A) 13 The static seismic definitions such as UBC, IBC, etc. have been
updated to ensure that any factor assigned to a selfweight mass is correctly
accounted for.
A) 14 The AISC 360-05 steel design module has been improved in the
design of pipe sections. Which were being designed as slender under all
conditions even when they should be consider as compact or semi-compact, thus
resulting in potentially conservative designs.
A) 15 The one way option of the FLOOR LOAD command has been updated to
account for the inclusion of FLOOR DIAPHRAGM commands in the file.
A) 16 The AITC 1994 and Mexican LRFD steel design codes have been
updated to correctly handle the parameter CMB which was not being used.
A) 17 The automatic wind loading routine has been updated to ensure that
the loading on HSS round sections in the standard databases and cold formed
round sections are loaded correctly as outlined in the online help.
A) 18 An additional message has been added to the IS:800-1984 code when
designing double I sections. This warns that these sections will only be
designed for the provisions of the general I section and does not account for
lacing or batten design.
A) 19 The BS5950:1-2000 steel design module has been updated for the
design of user defined I sections. The LTB slenderness of a user defined I
sections, the equations being used were that for sections with equal flanges
(section B.2.3 of the code). This could give rise to inconsistencies for user
defined I sections with unequal flanges. The design of I sections with unequal flanges
has been updated so that the equivalent slenderness will be calculated as per
section B.2.4 of the code.
A) 20 The iterative analysis that utilises both the MEMBER TENSION
setting and includes a MEMBER REDUCTION in the axial direction has been improved
to ensure that each iterative step includes the specified reduction factor.
Previously this was not done on all steps and could result in the iterative
solution not being achieved.
A) 21 The IS:800-2007 code has been updated to calculate the slenderness
of tee section profiles so that they can be included in a design. It should be
noted that sections currently defined as tapered sections with a bottom flange
as zero is not a correct method for defining a tee section. To be correct,
these should be defined using the Tee User Provided Table.
A) 22 The CABLE ANALYSIS has been updated to address occurrences which
would cause the analysis to crash.
A) 23 The IS:800-2007 design module has been updated to ensure that the
spacing of transverse stiffeners when set with the TST setting the value
specified in TSP is used. Additionally the calculation of D/Tw has been
corrected to use the web thickness rather than the flange thickness.
A) 24 The NRC 2005 seismic output has been modified to correctly
reference "Design Spectral Acceleration" where previously it had
referenced "Sec. Seismic Response Factor".
A) 25 The basic analysis engine has been updated to handle models that
include the legacy method for defining a finite element mesh using the commands
DEFINE MESH and GENERATE ELEMENT which was causing the analysis to crash.
A) 26 The IS:456-2000 concrete design module has been updated to ensure
that if the parameter ENSH is set to 1 then it will ignore the enhanced shear
check.
A) 27 The AISC 360-10 steel design module has been updated such that a
slenderness check is no longer used as a critical member ratio check. If a
slenderness check is included and exceeds unity, then it may be reported as the
governing criteria. However, if it is less than unity, then it will be
reported, but not used as the governing ratio.
A) 28 The processing of GROUP commands has been improved since the
addition of the RIGID FLOOR command to STAAD.Pro which caused an error in the
correct processing of the GROUP command.
A) 29 Generally MASS reference load type is used for the purpose of
forming the mass model of the structure for any seismic/response/time history
loading. In absence of this ref load case, the previous method of mass
modelling should be followed. However when rigid floor diaphragm definitions
are present, the program accepts Gravity ref load types to form the mass model
in absence of Mass ref load type. In absence of both Mass and Gravity ref load
types, the program will combine all Dead and Live ref load types to form the
mass model.
A) 30 The SOFT STORY CHECK has been updated to address when the master
joint on a rigid floor diaphragm is already defined as an analytical joint in
the model and thus no new joint is created as the master joint by the program,
then the program failed to calculate story stiffness correctly which is now
addressed.
A) 31 The one-way floor loading routine has been improved for
non-rectangular panels. This addresses he situation where the incidence of a
beam is reversed and a concentrated load was applied.
A) 32 The AIJ seismic loading has been updated to account for the
inclusion of the optional factor (f5) which is included in the addition of the
AIJ seismic definition in a load case.
A) 33 The NORSOK N004 steel design module has been updated to ensure that
when calculating the interaction ratio to Cl. 6.3.8.2 (Eq.6.27), the program
uses the applied axial load for the “NSd” term in the equation. The module was
previously using the axial capacity rather than the applied load for the
"NSd" term.
A) 34 The AIJ 2005 steel design module has been updated to ensure that
the calculation of the capacity uses the correct equation of either 5.12 or
5.14 when a value is specified in the CB parameter. Previously the choice of
equation was taken assuming the end moments to be zero and hence could produce
a lower capacity for the member and thus result in a conservative design.
A) 35 The IS800:2007 steel design has been updated to ensure that the
results of members that have been defined as double angle profiles are displayed
in the post-processing mode. The results of these members was previously only
shown in the output file.
A) 36 The automatic floor load command has been updated to ensure that
if the command SET FLOOR LOAD TOLERANCE has not been set, then a default tolerance
of 0.001 inches will be used.
(B) Issues addressed in the Pre-Processing Mode (03)
B) 01 The assignment of properties to an edit list has been updated to address
the occasional problem where if this is done on an existing list, the resulting
list would include a number of duplicate references.
B) 02 The GUI has been updated to ensure that if a LARGEDELTA parameter
is included in the PDELTA command, then it is retained when the file is saved
in the GUI.
(C) Issued Addressed in the Post-Processing Mode (01)
C) 01 The Post Processing of models creating large amounts of results data in
excess of 2 GB has been improved which would have previously reported an issue
of the form 'Unable to create mapping of the file c:\...\filename.ejt'
C) 02 The GUI has been updated to ensure that when the details of AISC
pipe sections are displayed in the member query and stresses displayed in the
post processing mode, unit conversions are applied correctly. A problem would
manifest itself if the base unit was not set to English or the current units
were not the default English units.
(K) Issues Addressed with Printing and Documentation (06)
K) 01 The analysis output has been enhanced with a summary of the number of
joints, members, plates, solids, surfaces and supports in the current model in
the Problem Statistics.
K) 02 Section 7C.5.4 of the International Codes Manual has been updated
to show the correct equation for structural hollow sections.
K) 03 Section 5.31.2.2 of the online help has been updated to clarify
the order in which weight definitions should occur in a seismic definition.
K) 04 The documentation of Example 21 in the Application Example manuals
has been updated to clarify the correct use of the MEMBER TENSION command.
K) 05 The OpenSTAAD documentation for the function Load.GetNodalLoads
has been updated to correct the type for the node number which should be a
long, rather than integer.
K) 06 The OpenSTAAD documentation has been updated to include details on
the function Output.GetIntermediateMemberForcesAtDistance with the syntax,
parameter list and example.
(L) Issues Addressed with licensing / security / installation (01)
L) 01 When a file is sent to be analysed any design blocks that are currently
not licensed with a suitable SELECT license (indicated with green dots on the
start page) are reported with a new message "Selected license set does not
support design code. The design will not be performed."
![]()
![]()